Securing Vue Apps with Keycloak
In this article we'll be using Keycloak to quickly secure a Vue application with user management and single sign on (SSO) using the open source IAMs Keycloak for Authentication and Authorization. We will demonstrate the integration by securing a page for logged-in users. This quickly provides a jump-off point to more complex integrations.
If you just want to skip to the code, visit the Phase Two Vue example.
Setting up a Keycloak Instance
Instructions
If you already have a functioning Keycloak instance, you can skip to the next section.
Rather than trying to set up a "from scratch" instance of Keycloak, we're going to short-circuit that process by leveraging a free Phase Two Starter instance. The Starter provides a free hosted instance of Phase Two's enhanced Keycloak ready for light production use cases.
-
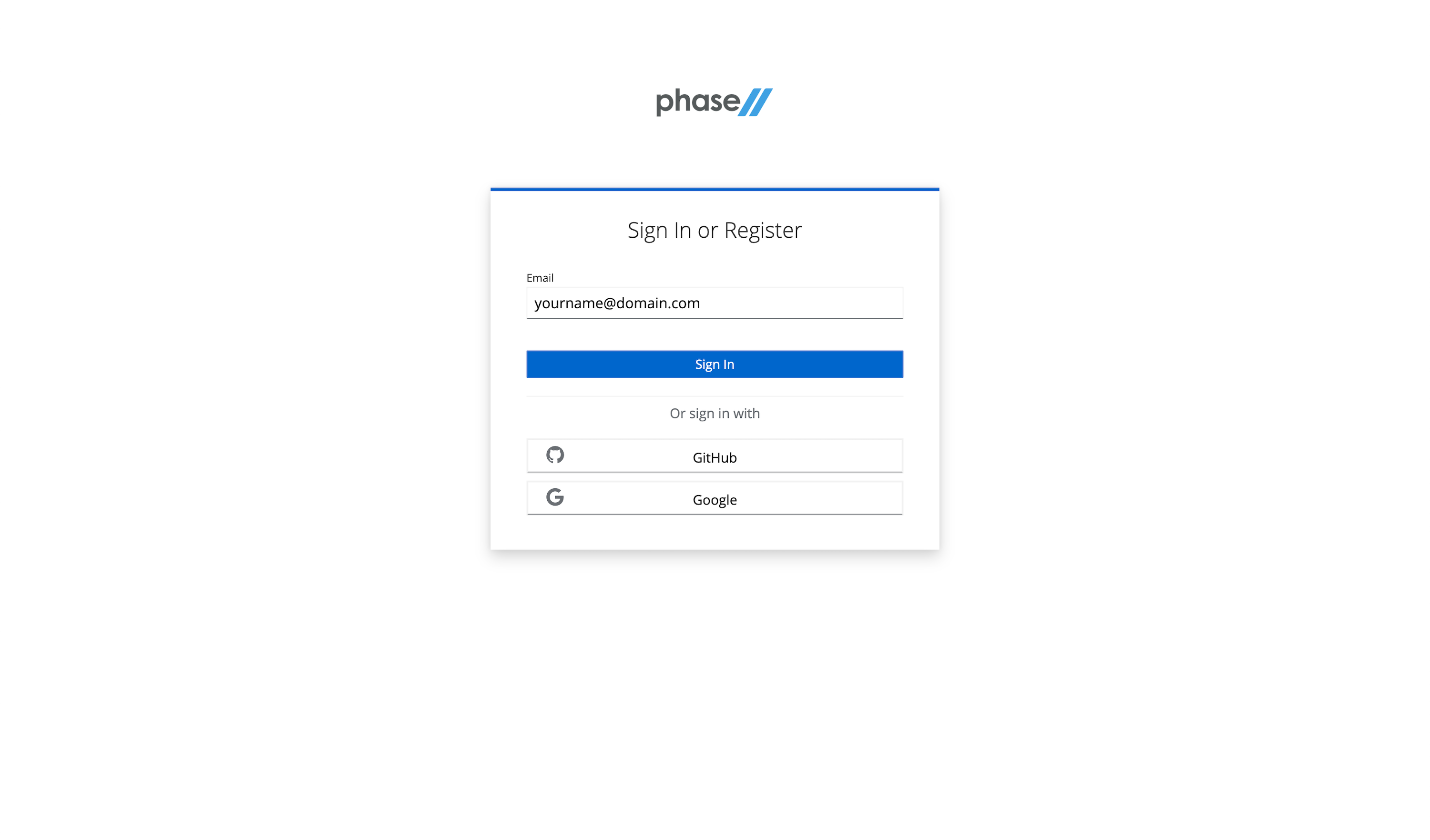
Visit the sign-up page.
-
Enter an email, use a Github account, or use an existing Google account to register.
-
Follow the register steps. This will include a sign-in link being sent to your email. Use that for password-less login.

-
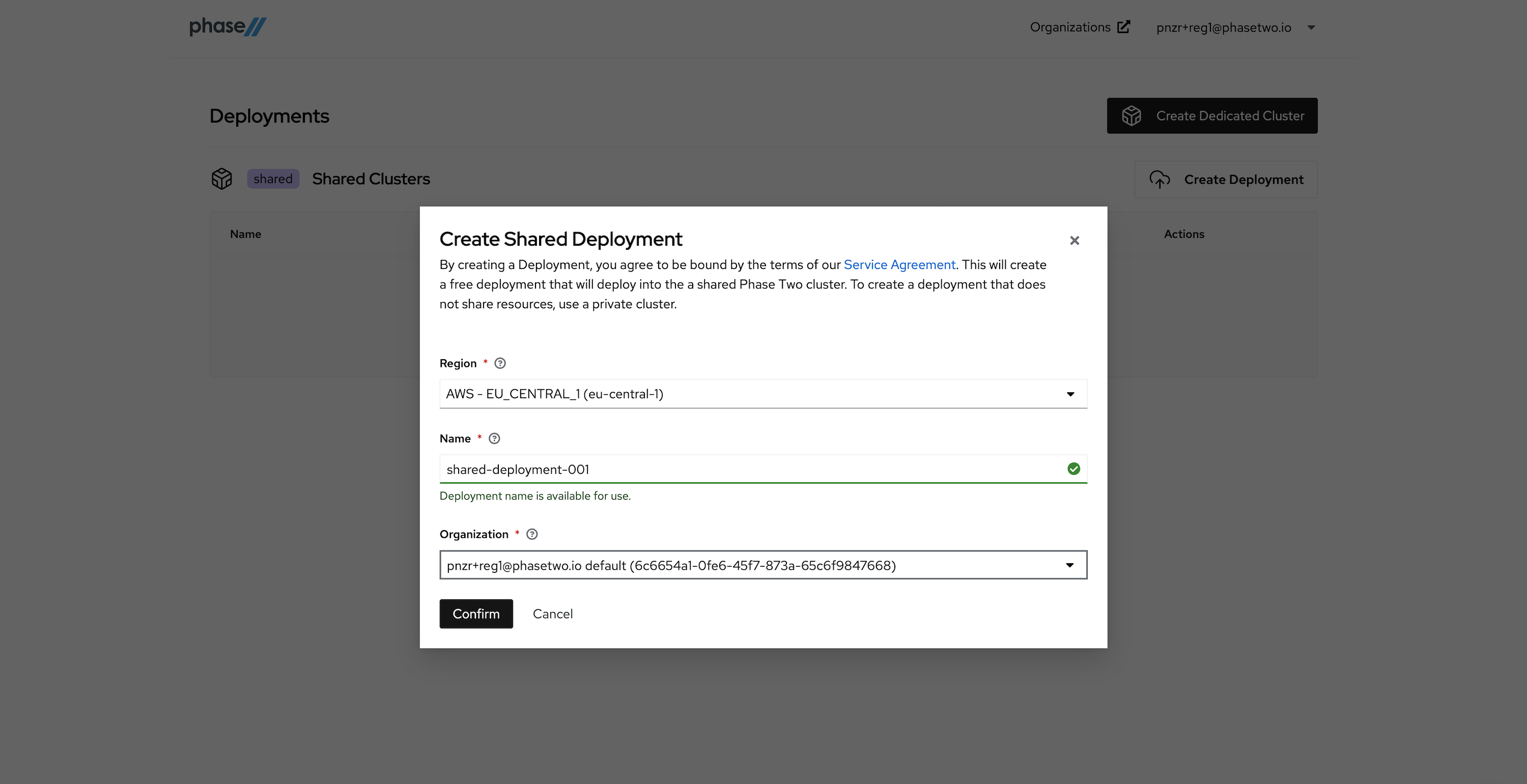
After creating an account, a realm is automatically created for you with all of the Phase Two enhancements. You need to create a Deployment in the Shared Phase Two infrastructure in order to gain access to the realm. Without a deployment created, the Create Shared Deployment modal will automatically pop up.
-
Create a Shared Deployment by providing a region (pick something close to your existing infrastructure), a name for the deployment, and selecting the default organization that was created for you upon account creation. Hit "Confirm" when ready. Standby while our robots get to work generating your deployment. This can take a few seconds.
-
After the deployment is created and active, you can access the Keycloak Admin console by clicking "Open Console" for that deployment. Open it now to see the console.
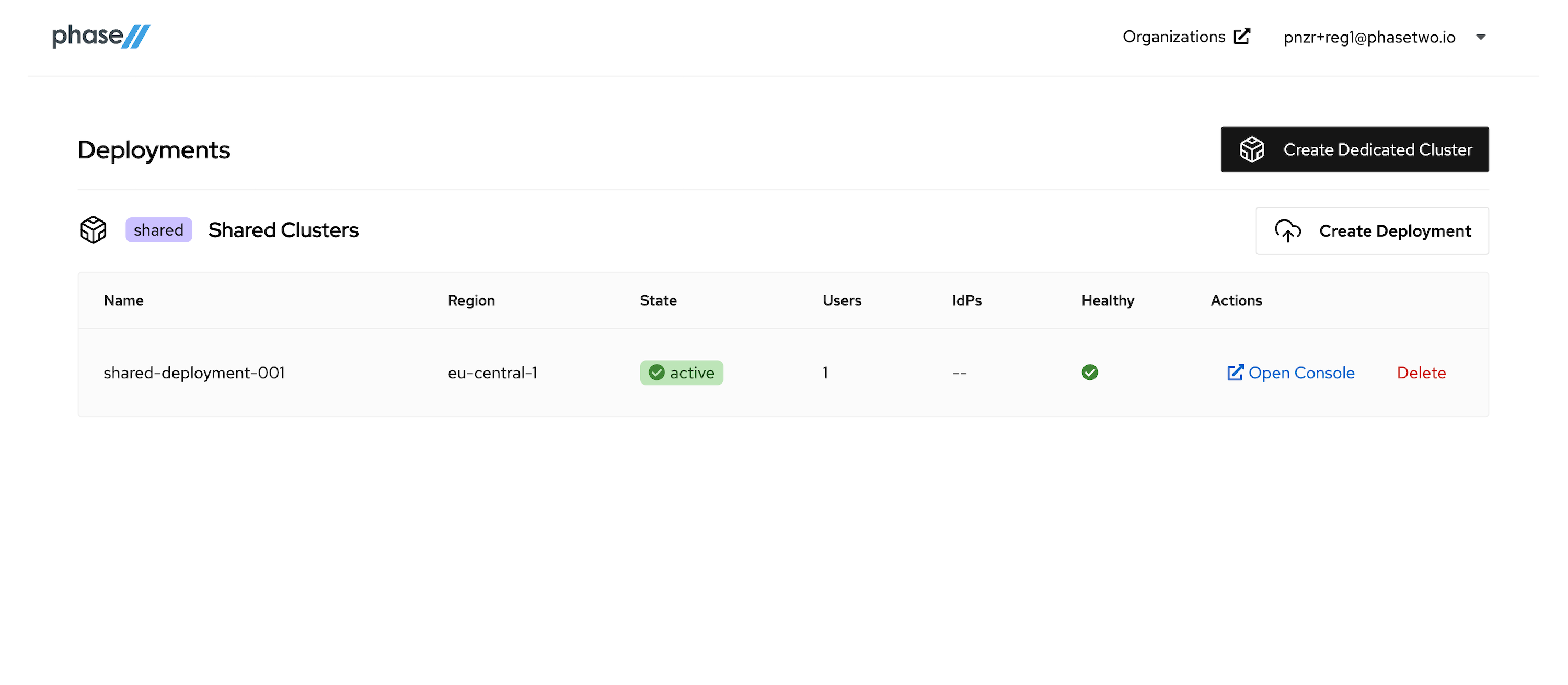
At this point, move on to the next step in the tutorial. We'll be coming back to the Admin Console when its time to start connecting our App to the Keycloak instance.
Setting up an OIDC Client
Instructions
We need to create a OpenID Connect Client in Keycloak for the app to communicate with. Keycloak's docs provide steps for how to create an OIDC client and all the various configurations that can be introduced. Follow the steps below to create a client and get the right information necessary for app configuration.
-
Open the Admin UI by clicking Open Console in the Phase Two Dashboard.
-
Click Clients in the menu.
-
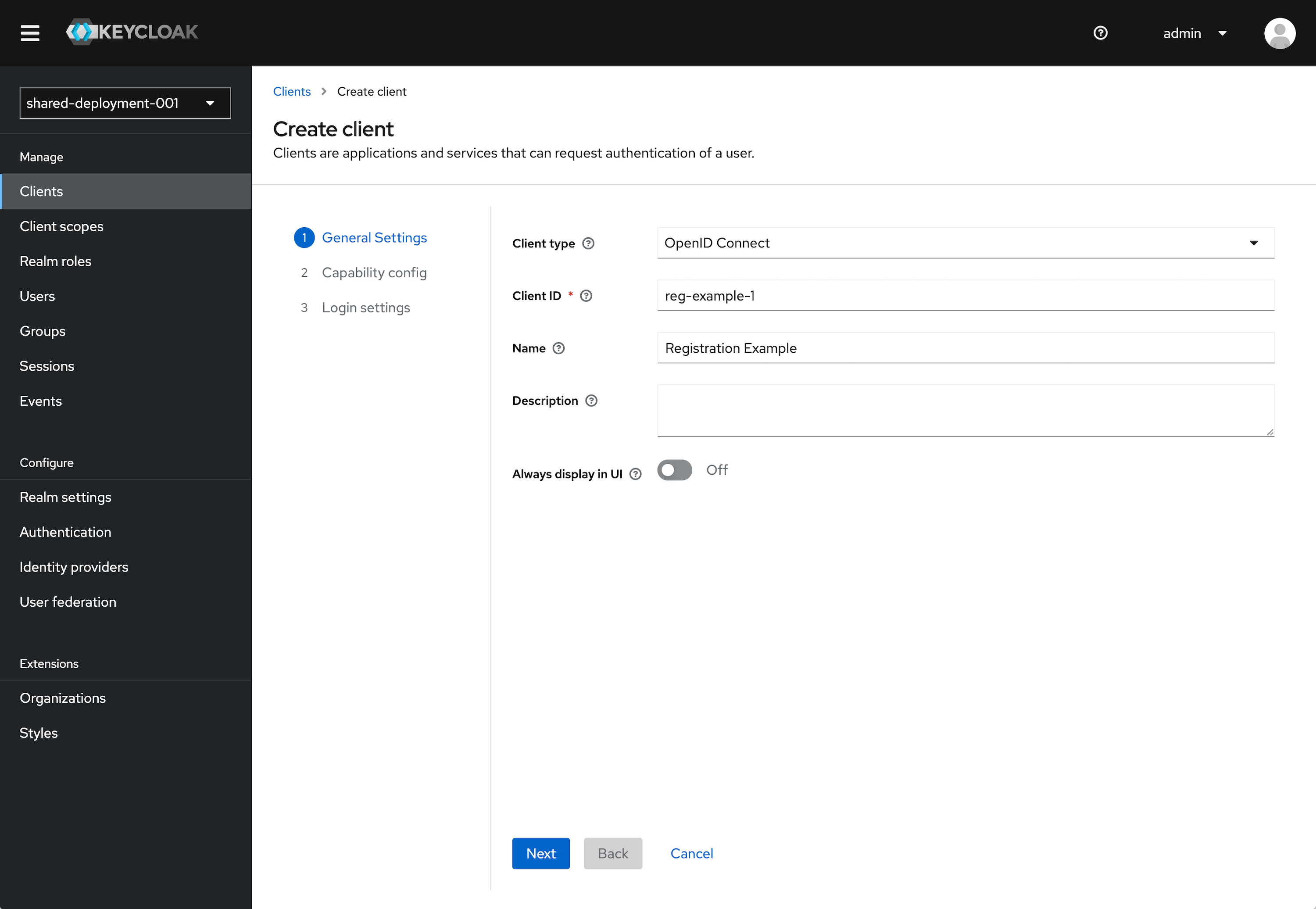
Click Create client.
-
Leave Client type set to OpenID Connect.
-
Enter a Client ID. This ID is an alphanumeric string that is used in OIDC requests and in the Keycloak database to identify the client.
-
Supply a Name for the client.
-
Click Next.
-
Under the Capability Config section, leave the defaults as selected. This can be configured further later.
- Client authentication to On.
- Authorization to Off.
- Standard flow checked. Direct access grants checked. All other items unchecked.
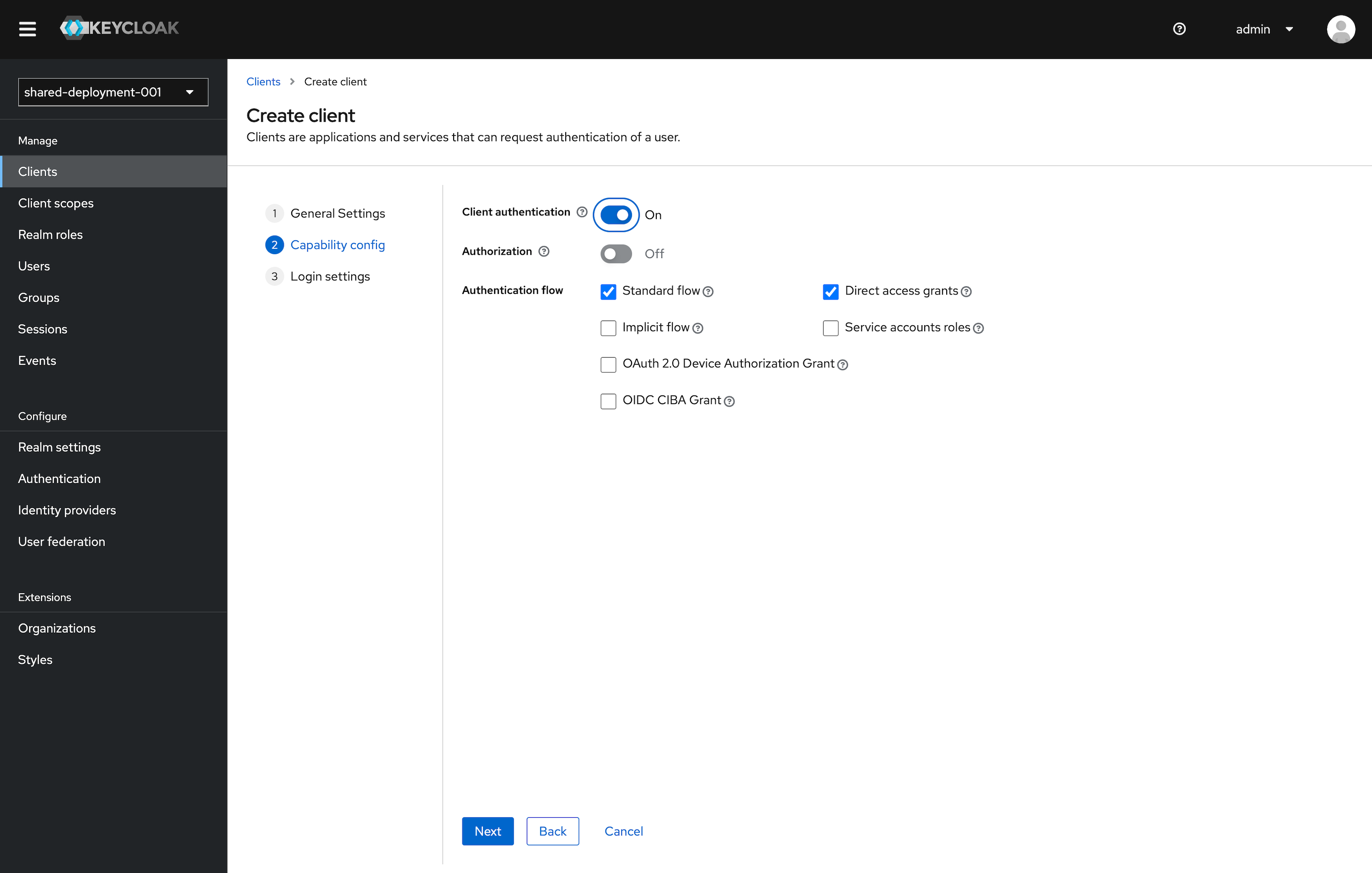
Click Next.
-
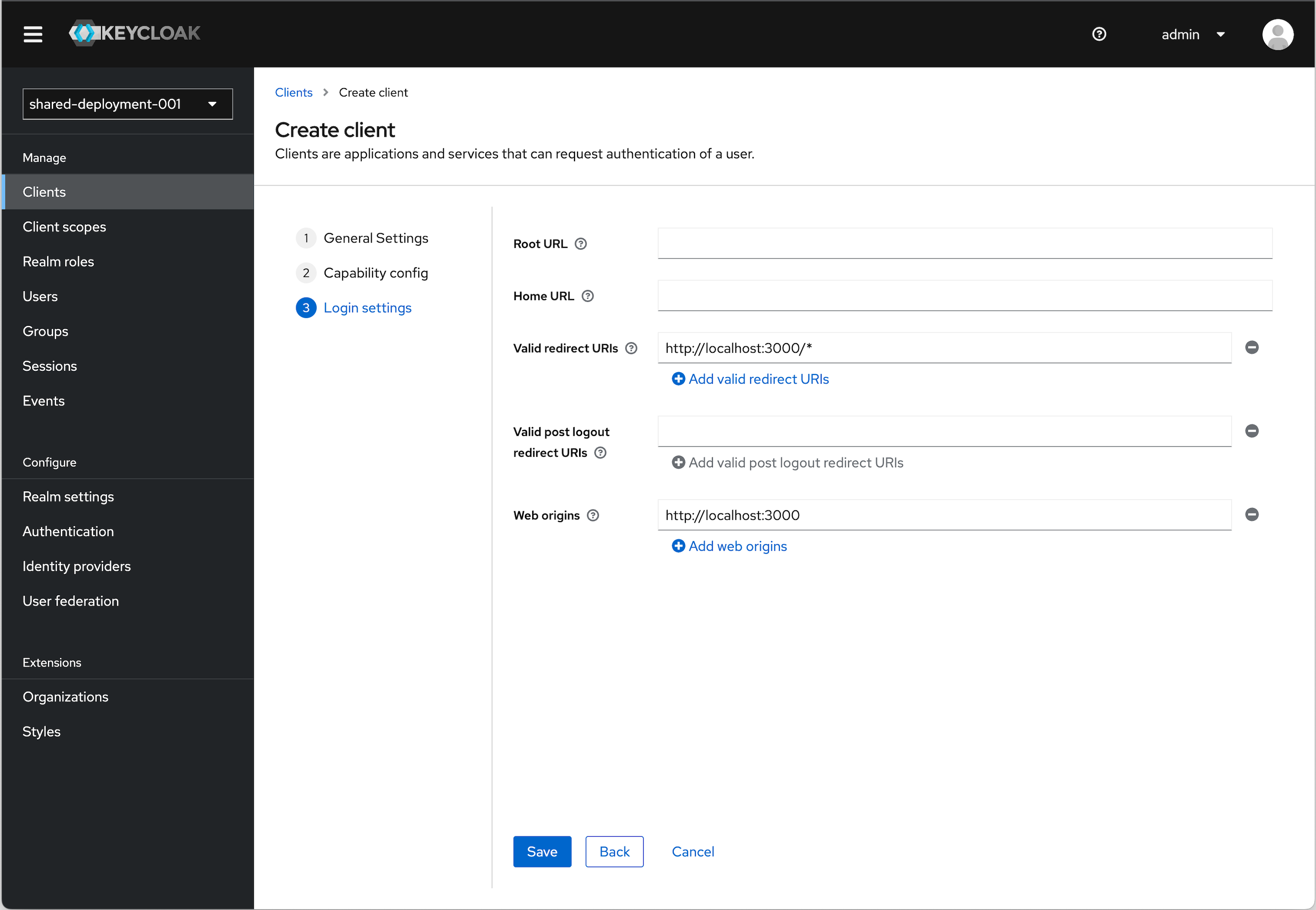
Under Login settings we need to add a redirect URI and Web origin in order. Assuming you are using the example applicaiton:
Valid redirect URI (allows redirect back to application)
http://localhost:3000/*Web origins (allows for Token auth call)
http://localhost:3000URI and Origin Details
The choice of
localhostis arbitrary. If you are using an example application running locally, this will apply. If you are using an app that you actually have deployed somewhere, then you will need to substitute the appropriate URI for that. -
Click Save
OIDC Config
We will need values to configure our application. To get these values follow the instructions below.
-
Click Clients in the menu.
-
Find the Client you just created and click on it. In the top right click the Action dropdown and select Download adapter config.
-
Select Keycloak OIDC JSON in the format option. The details section will populate with the details we will need.
- Note the
realm,auth-server-url, andresourcevalues.
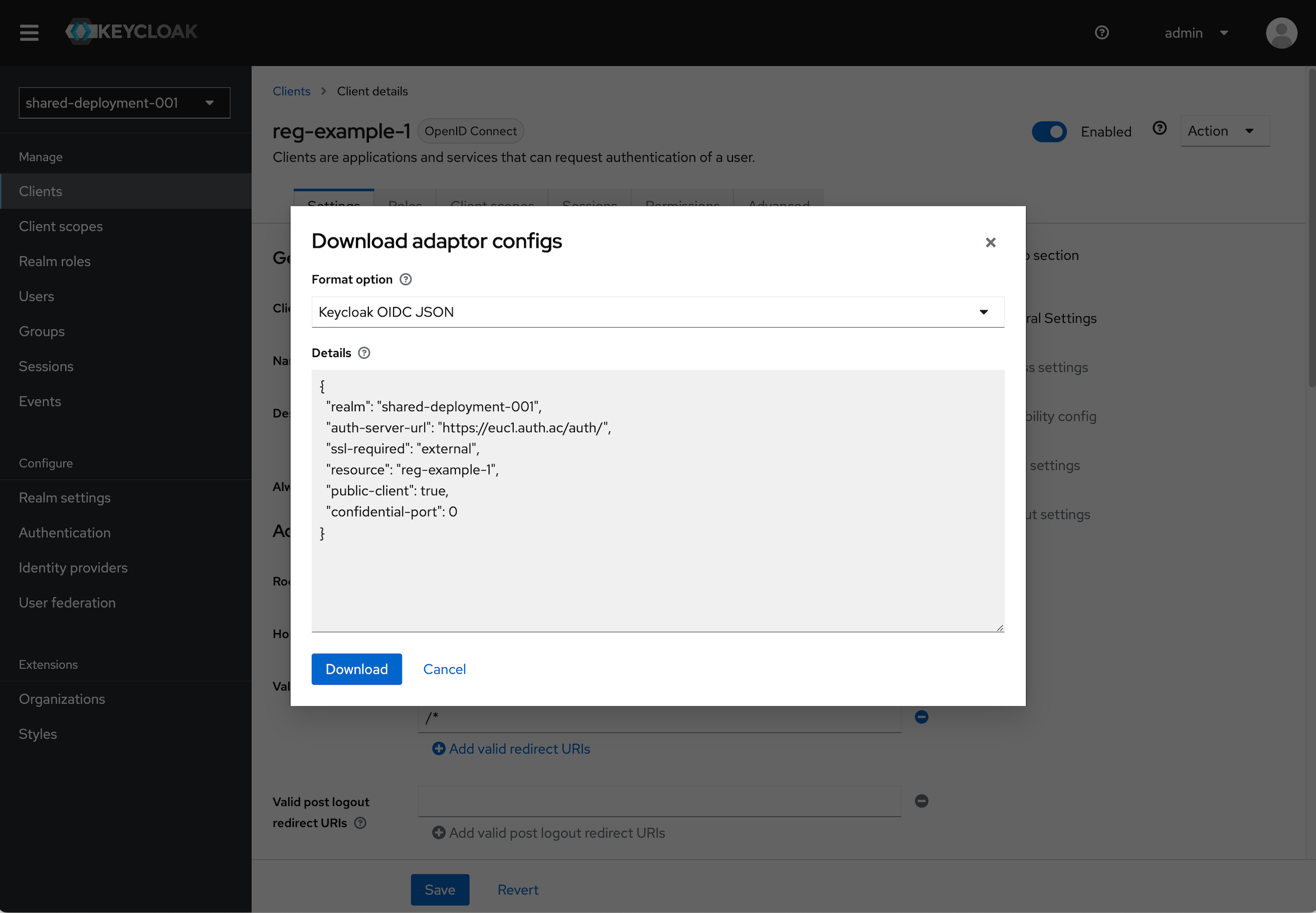
- Note the
-
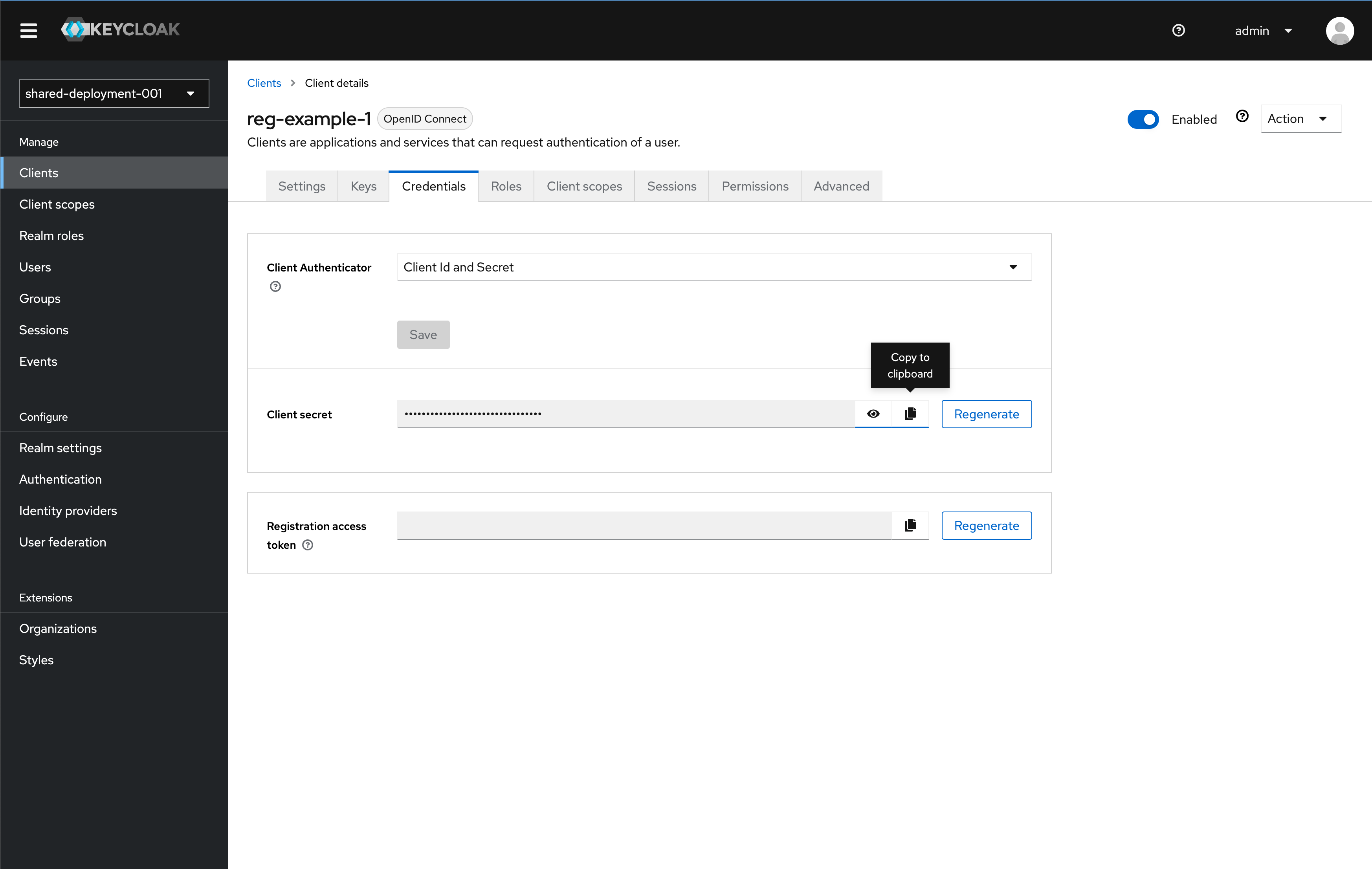
You also need to copy the Client secret in the Credential tab for the client to use. Once on the Credential tab, click the copy button to copy the key to your clipboard. Save the key somewhere for use later in this tutorial
Adding a Non-Admin User
Instructions
It is bad practice to use your Admin user to sign in to an Application.
Since we do not want to use our Admin user for signing into the app we will build, we need to add a another non-admin user.
- Open the Admin UI by clicking Open Console in the Phase Two Dashboard.
- Click Users in the menu.
- Click Add user.
- Fill out the information for Email, First name, and Last name. Click Create.
- We will now set the password for this user manually. Click Credentials (tab) and click Set Password. Provide a password for this user. For our use case, as a tutorial, you can leave "Temporary" set to "Off".
- Click Save and confirm the password by clicking Save password
Setting up a Vue.js Project
We will use the Phase Two Vue example code here, but the logic could easily be applied to any existing application.
This example uses Vue.js. We're going to leverage oidc-client-ts to integrate OIDC authentication with the Vue app. The oidc-client-ts package is a well-maintained and used library. It provides a lot of utilities for building out a fully production app.
-
Clone the Phase Two example repo.
-
Open the Vue folder within
/frameworks/vueand open the/nuxt/oidc-client-tsfolder. -
Run
npm installand thennpm run dev. -
We'll review where we configure out Keycloak instance. First open
/auth.ts. In this file you will want to update it with the values for the Keycloak instance we set-up earlier in the tutorial. Update theclientSecretwith the value. Use and environment variable here if you wish.export const keycloakConfig = {
authorityUrl: "https://euc1.auth.ac",
applicationUrl: "http://localhost:3000",
realm: "shared-deployment-001",
clientId: "reg-example-1",
clientSecret: "CLIENT_SECRET",
};After the config, you can see how the OIDC instance is started.
const settings = {
authority: `${keycloakConfig.authorityUrl}/auth/realms/${keycloakConfig.realm}`,
client_id: keycloakConfig.clientId,
client_secret: keycloakConfig.clientSecret,
redirect_uri: `${window.location.origin}/auth`,
silent_redirect_uri: `${window.location.origin}/silent-refresh`,
post_logout_redirect_uri: `${window.location.origin}`,
response_type: "code",
userStore: new WebStorageStateStore(),
loadUserInfo: true,
};
this.userManager = new UserManager(settings); -
With the Keycloak instance defined, we attach this to the app instance for Vue. Switch to
/main.tsimport Auth from "@/auth";
// ...
app.config.globalProperties.$auth = Auth;We pull in the
Authinstance then expose it through the$authvariable. -
There are a few main pages in play here that we define to create paths the library can leverage. The
/view/authand/view/silent-refreshcreate paths at the same name. These are used to do the redirection during authentication. From within these we use theAuthinstance to direct the user around within the app. For instance in/views/AuthView:export default {
name: "AuthAuthenticated",
async mounted() {
try {
await this.$auth.signinCallback();
this.$router.push("/");
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
},
};The
router.pushnaively sends someone to the home page. This could be updated to go to any number of places, including the page one started the login flow from if you were to store that information to be retrieved. -
Now that we have all the things setup, we can define the user component
/components/Userto easily pull information about the user's state and display the appropriate UI.export default {
name: "UserComponent",
data() {
return {
user: null,
signIn: () => this.$auth.signinRedirect(),
logout: () => this.$auth.signoutRedirect(),
};
},
async created() {
const user = await this.$auth.getUser();
if (user) {
this.user = user;
}
},
};With this, the user object is now easily available. A simple
v-if="user"allows the app to determine what UI to show.
Learning more
Phase Two's enhanced Keycloak provides many ways to quickly control and tweak the log in and user management experience. Our blog has many use cases from customizing login pages, setting up magic links (passwordless sign in), and Organization workflows.