Sample Application
Most users will want to get started quickly with a sample of how to secure an application. Once you have registered for a Phase Two account, you can clone our demo app repository to see a demonstration of authentication in action.
https://github.com/p2-inc/debug-app
Client setup
Before you configure and start the sample application, you must build a Client configuration. In Keycloak, a "Client" is synonymous with an application you are securing.
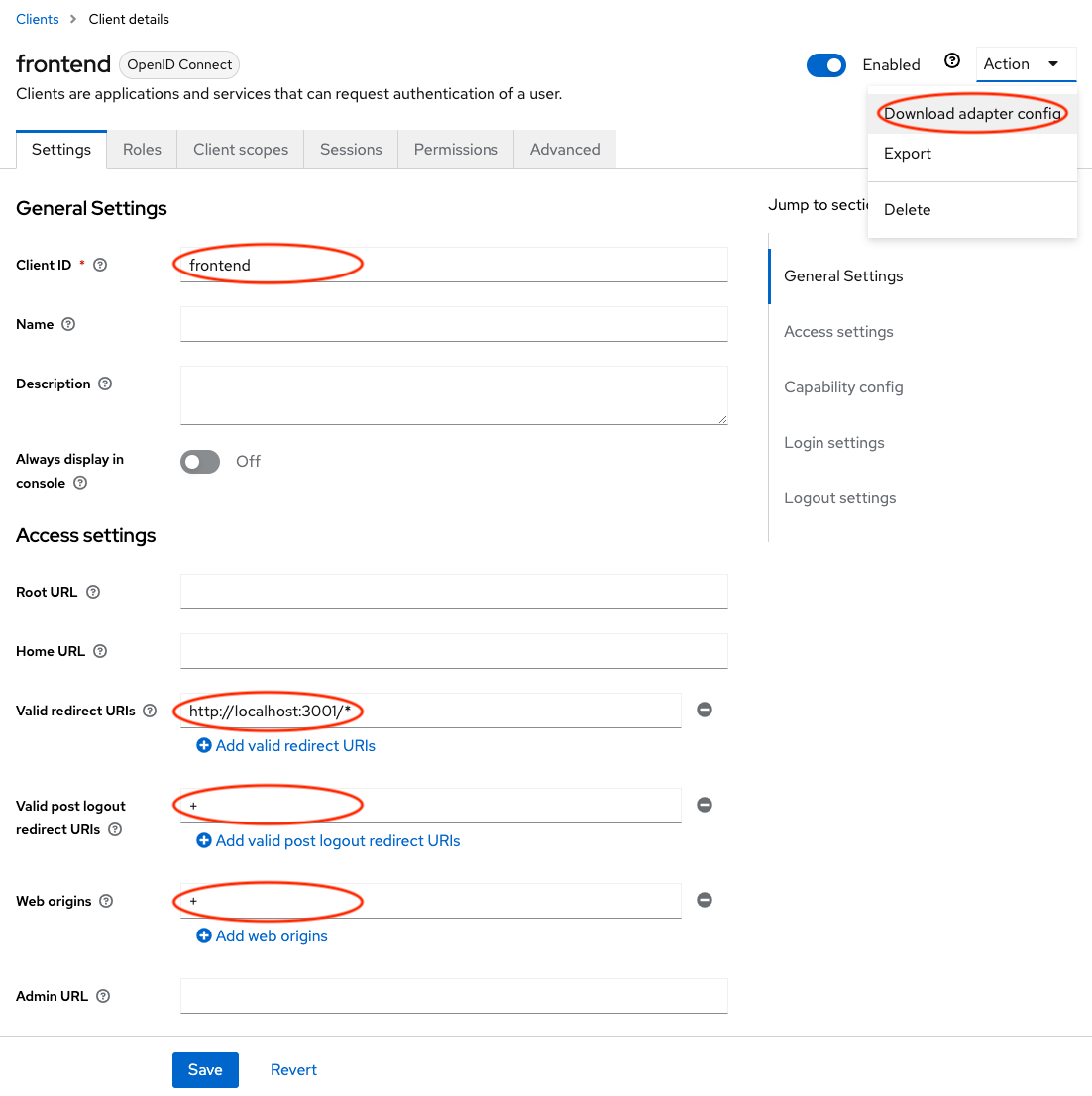
Log into your Keycloak realm, and click on Clients in the left navigation, and click Create client.
- Enter
frontendas the Client ID and click Next (you can name this whatever you want) - In the Capability config screen, keep the defaults and click Save
- In the Access settings screen, enter the following values:
http://localhost:3001/*for Valid redirect URIs+in Valid post logout redirect URIs+in Web origins
- Click Save
- In the upper right corner, open the Action menu and select Download adapter config. Click Download and save the file for the next step.
Sample configuration
Clone that repo to your local machine. You'll find the applications in the frontend and backend directory, and a set of supporting files for configuration and deployment.
git clone https://github.com/p2-inc/debug-app.git
cd debug-app/frontend
Once you have cloned the repo, edit the keycloak.json file and switch it with the configuration you downloaded at the end of the Client setup. It should look something like this (you'll need to replace the values in curly braces).
{
"realm": "{realm}",
"auth-server-url": "https://{host}/auth/",
"ssl-required": "external",
"resource": "frontend",
"public-client": true,
"confidential-port": 0
}
Then run the server using the included script:
./start.sh
And open http://localhost:3001/ in your browser. Once you have logged in, you'll see some information about the user that is contained the "access token" (more about that later).
Curious how it works? Most of the functionality for quickly securing an app is contained in app.js. More detailed information is contained in the next section, dedicated to securing applications.